The Satiety Secret: Building Meals for Lasting Fullness
This article delves into the art of meal composition aimed at maximizing satiety. We explore how incorporating specific nutrients, mindful eating practices, and the role of psychological strategies can extend the sensation of fullness after eating, helping to control hunger and manage overall caloric intake. Moreover, the article discusses innovative food technologies designed to trigger physiological responses for prolonged satiety, and how modern apps like Workout Notepad can support these dietary efforts through exercise and nutrition tracking.
WN
By Workout Notepad
February 23, 2024
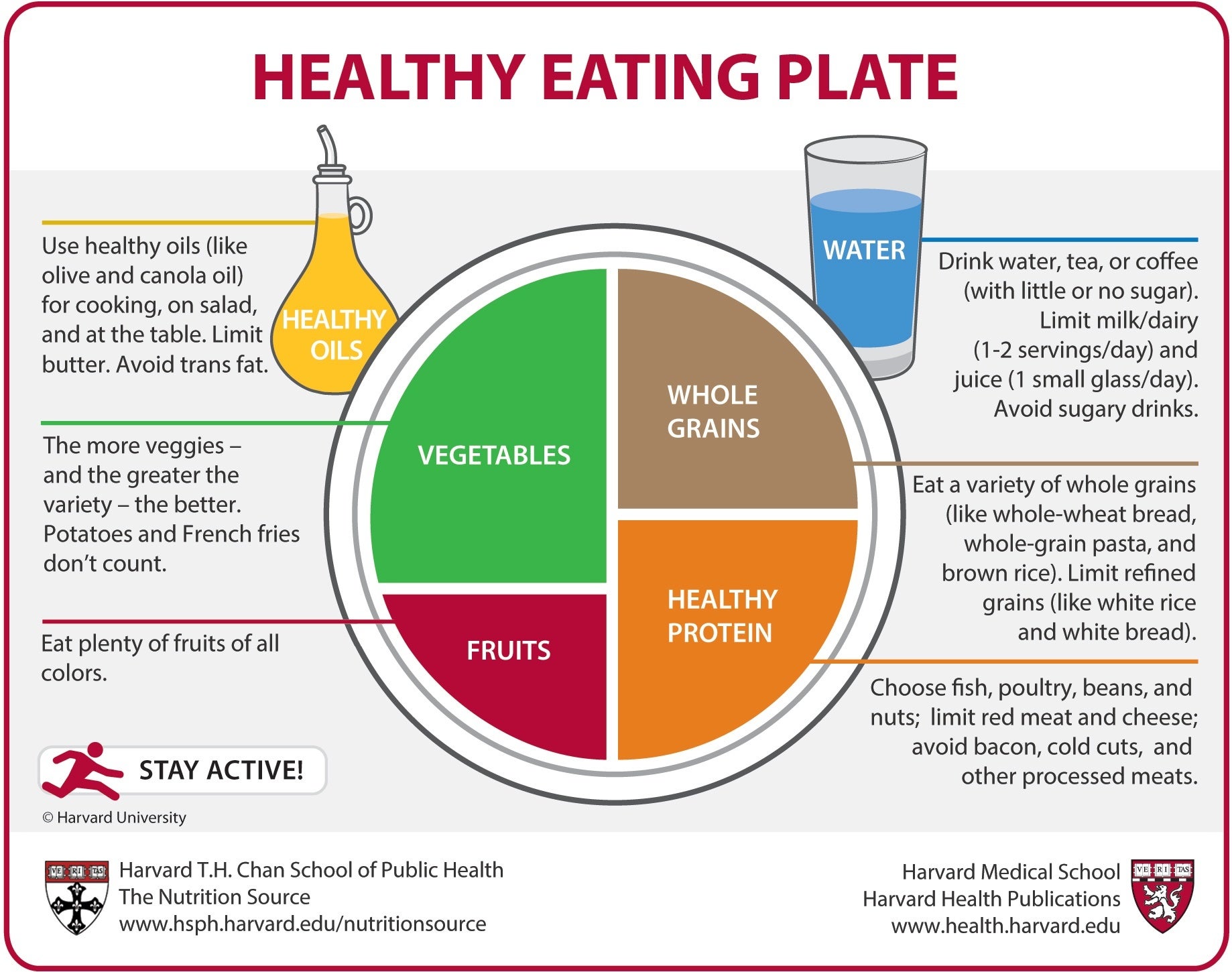
Satiety 101: Understanding the Fullness Factor
Satiety 101: Understanding the Fullness Factor
The quest for satiety—the sense of sufficiency and contentment after eating—is as old as humanity itself, linked to the pursuit of health and the maintenance of an energy-balanced lifestyle. Stemming from the Latin ‘satis’ for ‘enough,’ satiety epitomizes the point at which our bodies signal that our nutritional needs have been met, allowing us to step away from the dining table without feeling deprived. This physiological experience does more than just stop us from overeating; it plays a vital role in controlling our calorie intake, managing our weight, and sustaining our energy levels.
Indeed, not all foods are equal in the satiety stakes, with certain macronutrients throwing down the gauntlet against hunger. Protein and fiber emerge as victors in this realm, their complex structure copying the secret agent in a spy thriller—discreetly conscripting themselves to slow digestion and prolong the feeling of fullness. Introducing the concept of the ‘ileal brake,’ it becomes clear why these nutrients rank highly on the satiety index. As food reaches the latter stages of the small intestine, or ileum, triggers are activated that send signals of fullness to the brain, rousing the brake mechanism that signals satisfaction, decelerating hunger, and helping to manage our food intake with biological precision.
The Power of Protein and Fiber: Allies in Appetite Control
The Power of Protein and Fiber: Allies in Appetite Control
Hydration and Hunger: The Impact of Water on Appetite
Hydration and Hunger: The Importance of Water on Appetite
Proper hydration is crucial for health, and it plays a significant role in controlling appetite and food intake. Drinking water, specifically before meals, has been associated with reduced hunger and decreased caloric intake, primarily seen in normal weight individuals. Researchers speculate that water’s ability to induce feelings of fullness may discourage excessive eating, subsequently promoting weight management. Though the underlying mechanisms require further exploration, water’s potential as an accessory in appetite regulation cannot be ignored. Moreover, it’s worthwhile to highlight that the type of calories ingested can influence the extent of satiety: solid foods tend to induce greater feelings of fullness compared to liquid calories. This could be due to different physiological processes in digestion and the satiety signals triggered during and after consumption.
To practically incorporate water as a natural appetite control, one might start by drinking a glass of water 30 minutes before each meal which can lead to a moderate reduction in energy consumption. Keeping hydrated throughout the day also helps; often times, the body can mistake dehydration for hunger. Thus, responding to midday hunger pangs with water can help differentiate true hunger from mere thirst. Remember that replacing high-calorie beverages with water is another strategy that cuts down on liquid calorie intake without compromising fullness. While the adoption of such habits might differ in effectiveness among individuals and body types, it’s clear that incorporating water can be an uncomplicated step toward appetite control and a healthier lifestyle.
As the conversation shifts from the physical impacts of diet on satiety to the nuances of psychological influence, considering the mindfulness of consumption becomes paramount. The next section will delve into the cognitive facets of eating behavior, offering a perspective on how deliberate eating and awareness of psychological triggers can serve as powerful tools in the quest to understand and manage hunger effectively.
Mind Over Matter: Psychological Tricks for Reducing Hunger

mindful eating practice
Delving into the psychological aspects of eating unveils potent strategies for contending with the pervasive issue of knowing when to stop eating. Mindful eating, an approach that encourages paying full attention to the experience of eating and savoring each bite, embraces the idea of listening internally to the satiation cues our bodies provide. By slowing down the eating process and consciously appreciating the flavors, textures, and aromas of the food, individuals can align more closely with the signals from the left posterior amygdala, which monitors stomach volume and advises when it’s time to cease consumption. This mindfulness extends to recognizing hunger cues versus emotional or stress-induced eating, thereby supporting individuals in making more self-aware food choices, which can significantly reduce the likelihood of overeating.
By incorporating practices that foster a deeper connection between mind and body, such as stress management techniques and ensuring sufficient sleep, individuals bolster their capacity to control hunger effectively. Aligning oneself with one’s physiological needs by managing external stressors allows the body to function optimally, diminishing the misinterpretation of stress signals as hunger. Likewise, sleep quantity and quality have been shown to have a profound effect on hunger hormones like ghrelin and leptin. Ensuring an adequate amount of restful sleep can intercept the cycle of reaching for sustenance due to fatigue, thus granting individuals a more authentic gauge of their hunger levels. With these psychological methodologies, one is not only eating with awareness but living with it as well. The upcoming section will explore pioneering advancements in the food industry designed to directly harness satiety regulatory mechanisms, such as the ileal brake, providing innovative approaches to tackle the challenges of appetite management and energy intake.
Designing Foods for Fulfillment: The Future of Satiety
innovative satiety food products
Emerging advancements in the field of food technology are promising when it comes to enhancing satiety and managing appetite and energy intake. It is an interdisciplinary effort where the manipulation of food properties, such as texture and viscosity, reveals significant influences on our body’s satiety regulatory mechanisms, as discovered by Stribiţcaia and colleagues in their in-depth review. By engineering foods with considerations of food form and complexity, manufacturers aim to activate natural processes like the ileal brake—a physiological mechanism where nutrient-rich chyme from the stomach triggers hormone release in the latter part of the small intestine, amplifying feelings of fullness. This targeted approach could strategically reduce hunger and lead to better management of caloric consumption. The food industry, thus, stands on the cusp of integrating these research findings into marketable products that have the potential to battle the global overweight and obesity epidemic by appealing to consumers’ desire for satisfying, yet calorically appropriate, food choices. The intricate dance of integrating satiety-inducing ingredients and ensuring palatability poses a challenge, but given the current trajectory, it is one that many are eager to address.
In the context of building a bridge to satiety through lifestyle choices, active engagement in physical exercise presents another complementary avenue for appetite control. In the following section, we’ll examine how tying in regular physical activity with satiety can not only help in managing energy intake, but also in the overall holistic health of individuals. This exploration includes a look at technology’s role, such as how the utilization of apps like Workout Notepad to track fitness progress might relate to better satiety management and contribute to a healthier relationship with food and eating habits. Regular exercise routines carefully logged and monitored through such apps can bolster the psychological satisfaction from meals and amplify the physiological benefits of foods engineered for fulfillment. With the right tools and understanding, individuals have the potential to craft a satisfying dietary and lifestyle strategy that centers around comprehensive health and wellbeing.
Sweat It Out: Exercising to Keep the Hunger at Bay
Consistent physical activity stands out as a potent mechanism for appetite regulation, contributing to short-term energy deficits that do not provoke a compensatory increase in hunger. This acute effect on appetite, complemented by positive long-term influences on energy balance, aligns exercise with goals of satiety management. Engaging in regular workouts helps modulate appetite-related hormones and balance energy intake with expenditure, even though individual characteristics like body fat percentage and habitual activity levels may sway these responses. Intriguingly, the exercise-related adjustments in hunger and energy equilibrium appear to be generally uniform across different body types and genders, which reinforces the universality of exercise as a practical approach to maintaining satiety.
Utilizing tools like the Workout Notepad app, individuals can keep a closer watch on their physical activity regimens and their impacts on appetite control. By tracking exercise patterns and comparing them against fluctuations in hunger and energy intake, users gain a personalized insight into their unique satiety signals. The analytics and progression graphs offered by fitness-tracking apps can shed light on how specific exercise types or intensities influence an individual’s hunger cues over time—information that is crucial for tailoring a personal exercise plan that optimizes satiety. As we gear up for the next section of our article, we’ll pivot from the benefits of physical activity to practical dietary tactics, providing you with a robust understanding of how to strategically compose meals for amplified fullness and controlled caloric intake.
Constructing the Perfect Plate: Meal Composition for Maximum Satiety
To construct a meal that maximizes satiety, one must strategize the inclusion of high-protein, high-fiber foods, along with a balance of healthy fats. Starting your day with scrambled eggs, spinach, and whole-grain toast provides a high-protein kick coupled with fiber, which together work to keep you feeling full until your next meal. Lunch could be composed of a lean chicken breast over a bed of quinoa and roasted vegetables topped with avocado slices for your dose of healthy fats. Snacks incorporating Greek yogurt or a handful of nuts can serve as excellent high-satiety options between meals.
For dinner, think about incorporating a variety of colorful vegetables along with a source of lean protein such as grilled fish or tofu, and a side of sweet potatoes or legumes, which not only provide essential nutrients but also increase feelings of fullness. Foods that align with the satiating diet principles, such as those recommended by Diet Doctor’s higher-satiety meal plan, focus on the quality and fullness factor rather than calorie counting. Always listen to your body’s hunger signals, and you will be on your way to crafting satisfying meals that fuse the best practices of a satiety-focused dietary pattern. Remember, individual needs vary, so it’s important to adjust portions and food choices to fit your lifestyle and nutritional requirements for a well-rounded approach to health and satiety.
Your Personal Satiety Strategy: Combining Diet, Mindset, and Tech
In synthesizing the trove of information that we’ve meticulously detailed in this article, we’re left with several compelling strategies for conquering hunger and ensuring a lasting sense of satiety. Starting with the basics, Satiety 101 introduced us to the concept of the ‘fullness factor’, an essential guide to understanding how our bodies signal satiation. Progressing to the powerful combination of protein and fiber, we discovered their unmatched prowess in the realm of appetite control. Water’s influence on hunger was also uncovered, concluding that proper hydration can stave off false hunger cues. More subtle, yet equally significant, were the psychological strategies revealed in ‘Mind Over Matter’, teaching us to navigate the mental maze of hunger. The intriguing possibilities of ‘Designing Foods for Fulfillment’ hinted at a bountiful future, while ‘Sweat It Out’ reminded us of the integral role of exercise in maintaining appetite control. Finally, ‘Constructing the Perfect Plate’ provided tangible advice on meal composition and planning for peak satiation. A holistic satiety strategy isn’t just a patchwork of diet tips; it’s a sophisticated integration of nutritional science, mental resilience, and utilizing technology to its fullest. Much like the intricate process of satiety itself, weaving these aspects into one’s routine can spell the difference between fleeting fullness and profound, sustained satisfaction.
As you endeavor to tailor a personal satiety strategy, consider not merely the nourishment your body requires, but the psychological tactics that can keep pesky cravings at bay. Adapt the provided meal plans to your lifestyle and tastes, but also embrace tools like meal trackers or apps like Workout Notepad—that, while unrelated to diet—play an indirect role in managing your overall wellbeing. For instance, the convenience of logging your physical activity and the motivational aspects of seeing your progress can indirectly improve your consistency with exercise. This could be beneficial because physical fitness contributes positively to reducing hunger and sustaining energy levels. Engaging in this multifaceted campaign against unrelenting hunger will not only culminate in a more satiated state but wield a powerful influence on achieving your health and weight management goals. With sustained commitment and an array of strategies at your disposal, crafting a customized satiety strategy becomes not just a possibility, but a transformative life practice.
SOURCES
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/ways-reduce-hunger-appetite
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2771510/
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/wp-content/uploads/sites/30/2012/09/HEPJan2015.jpg
- https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/satiety
- https://dictionary.cambridge.org/us/dictionary/english/satiety
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6016687/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23885994/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29678599/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6209729/
- https://www.menshealth.com/uk/weight-loss/a41051180/10-ways-to-tame-your-appetite/
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/ways-reduce-hunger-appetite
- https://commwellhealth.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/6-ways-to-practice-mindful-eating.jpg
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7395742/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3662086/
- https://www.nordicinnovation.org/sites/default/files/styles/featured_cover/public/2019-09/Satiety_weightmanagementandfoods2009.PNG?h=3b0a23a2&itok=OZTX6KhF
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6164815/
- https://www.verywellfit.com/how-exercise-affects-appetite-5218713
- https://www.dietdoctor.com/satiety/meal-plan
- https://www.verywellfit.com/satiating-diet-4691353
- https://www.allcare.ae/health-tips/5simple-stepsfor-creatinga-personalized-diet-plan
- https://www.dietdoctor.com/satiety/meal-plan
