Neuromuscular Knockout: Next-Level Nerve Flossing Exercises for Mobility
Explore the benefits of nerve flossing exercises for enhancing mobility and reducing pain through next-level techniques. This article will navigate through the world of neural gliding, diving into specific exercises for various nerves, and providing insights into safe practice and effectiveness. It will also provide a subtle nod to the digital age of fitness tracking with a relevant solution for those looking to monitor their progress.
WN
By Workout Notepad
February 02, 2024
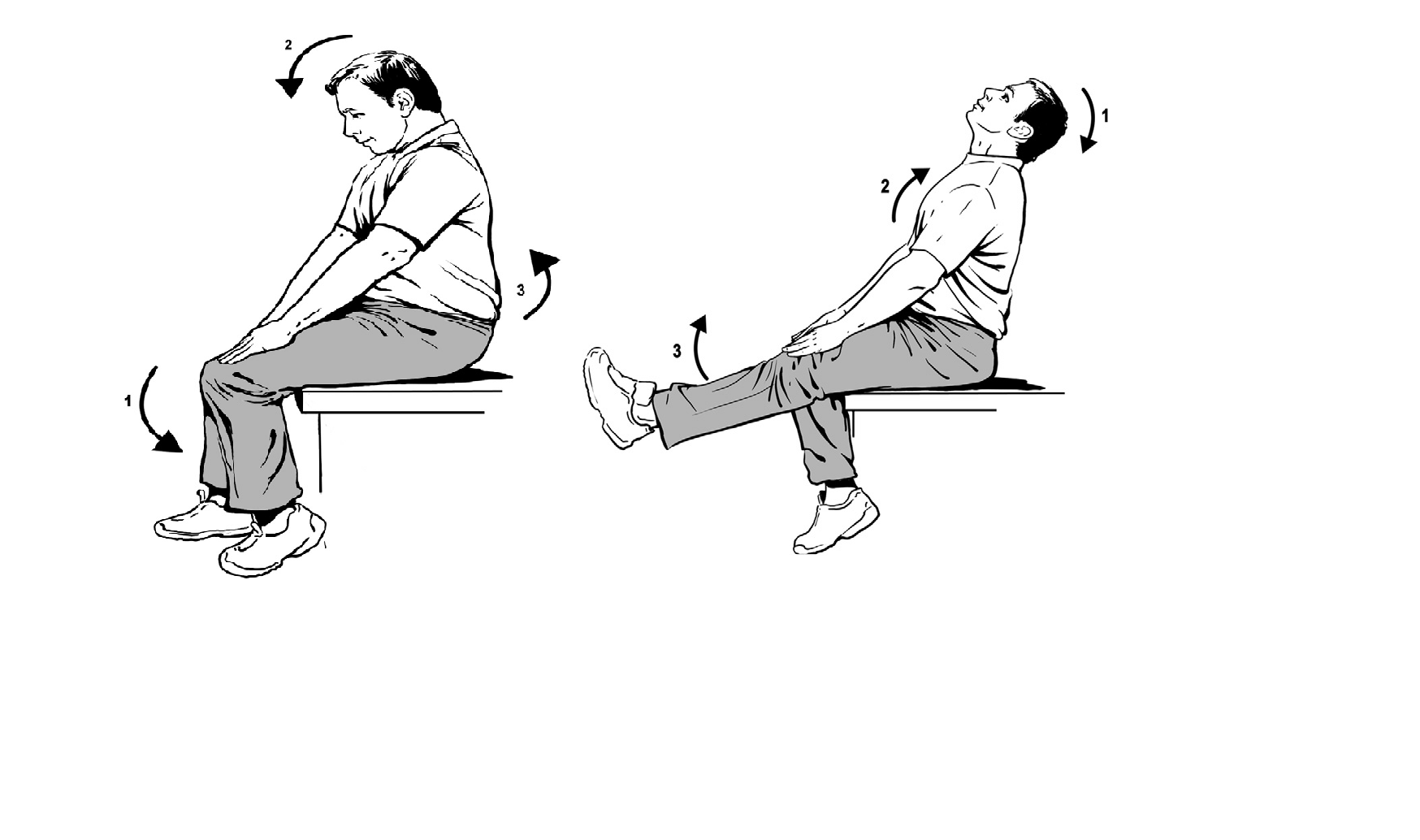
What’s All the Buzz About Nerve Flossing?
In recent years, an innovative conversation has gripped the corners of fitness gyms and rehabilitation clinics alike, centering around the intriguing methodology known as nerve flossing, or neural gliding. Billed as a physiotherapeutic breakthrough, nerve flossing is a type of exercise aimed at relieving symptoms associated with nerve impingements, such as pain and limited mobility. By applying gentle stretching and gliding motions to targeted nerves—namely, the sciatic, ulnar, median, femoral, and brachial plexus nerves—practitioners claim to help alleviate discomfort and enhance flexibility. The practice has garnered attention for its non-invasive approach and is often used alongside other treatments to manage conditions like sciatica and carpal tunnel syndrome. As a promising adjunct to traditional forms of physical therapy, nerve flossing offers a ray of hope for those struggling with nerve-related issues, spurring a trend that champions the virtue of inner harmony and neuromuscular well-being.
The allure of nerve flossing extends beyond anecdotal praise; it is rooted in the application of specific exercises designed to address the unique needs of various nerve pathways. Amidst this fascination rests an eagerness to comprehend the underlying science of nerve mobility. As enthusiasts embark on laying groundwork practices for this technique, the next section will delve into the compelling aspects of the physiological mechanics behind nerve flossing, unfolding the distinction between nerve tensioning techniques and the gentle, nurturing rhythm of nerve gliding which aims to sort these neural pathways in a manner akin to unraveling a tangled string of pearls, thus paving the way for increased serenity within the neuromuscular landscape.
The Science of Sliding: How Nerve Flossing Works

nerve gliding diagram
At the heart of nerve flossing lies its unique ability to facilitate the smooth gliding of nerves through the muscles and tissues within our body, akin to the way dental floss moves between our teeth. Unlike static stretches that extend the nerve and its surrounding structures, nerve flossing combines motion and stretch to help release nerve tension and improve mobility. The physiological premise is that nerves, as pliable structures, can benefit from these sliding motions, which promote blood flow and reduce the mechanical friction that may lead to irritation and pain. Physiologically, this process functions like a careful dance between tensioning and gliding – tensioning refers to the gentle stretch of the nerve while gliding pertains to the movement of the nerve through its surrounding sheath. When executed correctly, nerve flossing aims to mitigate issues associated with nerve impingements, such as numbness, tingling, and radiating pain by gently mobilizing the nerve without causing further irritation.
Moving from the mechanics to the application, nerve flossing manifests through various exercises, each targeting specific nerves for optimal outcome. Some exercise routines dial in on the neurodynamics of the sciatic nerve, running from the lower back through the buttock and down the leg, to relieve sciatica symptoms. Others might concentrate on the brachial plexus to alleviate discomfort related to issues in the shoulders, arms, or hands. Establishing the fine balance between tensioning and gliding in these exercises is crucial, and the subsequent section of this article will delve into how specific maneuvers are designed to, quite literarily, keep the nerves in motion. As you shift toward the ‘Target Practice: Exercises for Key Nerve Groups’ section, expect to discover how targeted nerve flossing exercises can serve to mobilize each area – providing clarity on what routines may successfully restore mobility and relief in afflicted nerves.
Target Practice: Exercises for Key Nerve Groups
Understanding the needs of different nerve groups is crucial in addressing their specific issues and optimizing the benefits of nerve flossing exercises. The sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back through the hips and down each leg, is often targeted to alleviate the discomfort associated with sciatica. Exercises designed for this nerve involve leg and foot movements orchestrated to prevent and relieve compression that can cause pain. The piriformis muscle, found in the gluteal region, can entrap the sciatic nerve, leading to piriformis syndrome; here, nerve flossing exercises aim to mobilize the nerve through stretching the hip muscles and improving sciatic nerve glide. Moving upwards, the median nerve, leading to the carpal tunnel in the wrist, requires a different set of flossing exercises. These can include wrist and finger flexions and extensions, serving to improve hand and wrist functionality, frequently affected by repetitive strains or injuries. Lastly, for the brachial plexus—a complex nerve network providing sensation and motor function to the arms and hands—exercises might involve shoulder, neck, and arm movements that encourage nerve mobility without triggering irritation or increased pain.
The execution of these exercises, pivotal for the mobilization and health of these nerve groups, should be approached with careful vigilance to techniques to ensure safety and efficacy. It is easy for individuals to inadvertently cause further distress to the nerves by straining or overly stretching, underlining the need for proper guidance, which will be discussed in the succeeding section. Here, we will venture into the specific do’s and don’ts, how to recognize when a technique is failing to benefit, and effective strategies to integrate nerve flossing into your daily routine without discomfort.
Doing It Right: Guidelines for Effective Nerve Flossing
Adopting correct techniques during nerve flossing is crucial for ensuring its effectiveness and preventing potential discomfort or injury. To start, it’s critical to avoid any motions that cause pain; nerve flossing should be a gentle process. Breathing rhythmically and deeply is essential as it supports the relaxation of muscles and promotes better circulation, which is pivotal for nerve health. Starting slowly is another key component—rushes into rigorous or forceful stretching can provoke further irritation of the nerves. Gradual progress and consistency are more beneficial than intensity when dealing with delicate neural tissues. Exercises should be performed within a comfortable range of motion, and attention should be paid to the body’s responses. If sharp pain, numbness, or tingling occurs during an exercise, it is recommended to stop immediately and adjust the technique or consult with a healthcare practitioner.
As essential as teaming up with professionals is for intricate health maneuvers like nerve flossing, pivoting into the realm of autonomous well-being monitoring, one should heed common missteps. Among those, a prevalent error is the neglect of individual nerve pathways; each nerve flossing exercise targets a specific nerve group and should be executed with that in mind. Another typical oversight involves the frequency and duration of exercises. While some individuals might be inclined to perform nerve flossing sporadically, establishing a regular routine can help garner the benefits, which typically manifest after six to eight weeks of consistent practice. Finally, incorporating slow and focused repetitions can often be more effective than aiming for quantity, which respects the nerve’s natural healing process. Remember, guidelines and precautions protect one from submitting to false perceptions of harmless glides; painful experiences suggest a halt and reassessment of method or a professional consult—precisely what the next section will explore in greater detail.
Consult the Pros: When to Seek Expert Advice

consultation with health professional
While the allure of self-treatment is ever-tempting, the importance of professional guidance cannot be overstated, especially regarding techniques like nerve flossing. Considering that specific exercises are recommended for different nerves, such as the sciatic, piriformis, median, ulnar, and radial nerves, the potential for exacerbating an issue is tangible. As such, one should consult a health practitioner before commencing any new nerve flossing routines, especially if conditions like sciatica or piriformis syndrome are present. Professionals can provide tailored advice that mitigates risks and maximizes the efficacy of nerve flossing. This preemptive step is crucial when there is severe pain during these exercises, as it could indicate an underlying complication that requires immediate medical attention. A practitioner’s endorsement serves as reassurance that the selected exercises are suitable for the individual’s specific condition and will contribute positively to their healing journey.
Evolving your self-care regimen necessitates not only an understanding of the correct techniques but also an awareness of when these efforts should be charted and evaluated for progress. In considering the expansion of one’s nerve flossing practice, it is constructive to reflect on the utility of meticulous documentation of one’s journey. The next section discusses the use of digital tools, like the Workout Notepad, which can play a pivotal role in tracking the crucial inconsistencies in pain levels and range of motion that can indicate either improvement or the need for a revised approach. By recording these details, individuals can provide their healthcare providers with valuable information, enhancing the collaborative effort in rehabilitation and personal fitness.
Tracking Your Success: The Role of Digital Tools
In the realm of rehabilitation and fitness, the act of monitoring and recording one’s progress is not merely a form of self-affirmation, but a strategic tool that can greatly enhance the effectiveness of one’s efforts. Leveraging digital tools has revolutionized how individuals track their physical advancements and recovery milestones. Through consistent documentation, patterns emerge that can inform future exercise adjustments, signal when to increase intensity or complexity, and celebrate achievements both big and small. Utilizing modern solutions such as the Workout Notepad app, which provides a multitude of tracking and analysis features, primes individuals for a more structured and data-driven approach to their fitness journeys. This allows for an intimate understanding of one’s own body, fostering a nuanced gauge of performance and recovery.
As individuals integrate nerve flossing routines into their overall fitness strategy, the ability to analyze each nuance of their progress becomes instrumental. Apps such as the Workout Notepad cater to this need by offering the ability to attach visual aids, like images or videos, to specific exercises or movements, aiding in the accurate replication of those exercises over time. By graphing exercise data, it becomes possible to readily visualize gains and setbacks, enabling users to tailor their regimens with unprecedented precision. The transition from manual tracking to this kind of sophisticated personal fitness documentation not only reinforces commitment but also sets a powerful stage for the next section of the discussion: the concrete benefits that individuals are experiencing with nerve flossing, as evidenced by recent studies into its efficacy.
Real Results: What Studies Say About Nerve Flossing
In navigating the maze of therapeutic options for managing pain and improving movement, nerve flossing has emerged as a topic of increasing interest within the rehabilitation community. Scrutinizing its efficacy, researchers have ventured into the realm of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) but have met with a tapestry of results that complicate the narrative. This systematic review of RCTs aimed to bypass anecdotal testimonies in favor of scientific rigor, only to confront the reality of methodological disparities and moderate-quality evidence, leaving us with a rather equivocal conclusion. The revelations from these studies underscore the impact of nerve flossing in real-life scenarios but hesitate to sing loud praises due to a conglomerate of diverse clinical approaches and non-standardized treatment interventions. Thus, while certain studies advocate for the short-term benefits of nerve flossing in alleviating pain and improving both function and flexibility, especially in adults with Low Back and Radicular Pain (LBRP), the chorus unfurls with caution, insisting on superior quality research to authenticate these promising flashes. Despite the different variables explored—pain, disability, function—the limited studies and their qualitatively varying designs present an incomplete picture, albeit one tinted with cautious optimism for nerve flossing’s potential in physical therapy realms.
As the discourse around nerve flossing continues to evolve with emerging studies, there remains an open invitation for future research to adopt more stringent and unified standards that will lead to clearer understanding and targeted treatment strategies. Paving a way forward involves acknowledging the need for precision and consistency in defining participant populations, intervention protocols, and combining robust clinical outcome measures with objective assessment of neural dynamics. This closing ecosystem of inquiry perfectly dovetails into the next vital step for individual enthusiasts and clinicians alike: crafting a tailored, evidence-based nerve flossing routine. The forthcoming section, therefore, not only promises to synthesize the exercises and guidelines discussed throughout this compendium but also aims to choreograph a personalized nerve flossing symphony that aligns with the unique contours of each individual’s recovery and wellness narrative.
Keeping It Moving: Crafting Your Nerve Flossing Routine
With a deeper understanding of how nerve flossing contributes to pain relief and improved flexibility, especially for those suffering from conditions like sciatica and piriformis syndrome, it’s time to apply this knowledge towards developing a personalized routine. The key is consistency and gentility: incorporate mobilizing stretches and seated sciatic nerve flosses into your daily regimen, making sure that each movement is conducted with slow, deliberate motions to avoid further irritation of the nerves. Remember, nerve flossing is envisaged as a gentle release of neural adhesions, and as such, should not be painful. Use nerve tension tests to identify specific areas of altered neurodynamics, and tailor your flossing exercises to target these spots, promoting the restoration of normal nerve function.
As with any exercise program, the effectiveness of your nerve flossing routine hinges on monitoring progress and making adjustments as needed. Take note of the exercises that provide the most relief and consider frequency adjustments to ensure ongoing benefit. Digital tools, such as a Workout Notepad or fitness tracking app, could be instrumental in keeping track of your exercises, their intensity, and frequency—although such tools are not a focus in the practice of nerve flossing, they may help with execution consistency for some individuals. Designing a routine that becomes a seamless part of your lifestyle is crucial for long-term improvement, and this often involves setting aside regular time slots dedicated to your nerve flossing exercises. With practice, perseverance, and the scientific backing that supports the effectiveness of therapeutic nerve flossing, you can create a sustainable routine that helps manage pain and enhances your range of motion, keeping you moving smoothly and efficiently.
SOURCES
- https://www.yorkvillesportsmed.com/blog/ultimate-guide-to-nerve-flossing-and-how-it-can-help-you
- https://chiroup.com/blog/4-simple-nerve-flossing-exercises-to-help-resolve-back-leg-pain
- https://www.disc-me.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/sciatic-1.bmp
- https://www.yorkvillesportsmed.com/blog/ultimate-guide-to-nerve-flossing-and-how-it-can-help-you
- https://www.healthline.com/health/nerve-flossing
- https://www.yorkvillesportsmed.com/blog/ultimate-guide-to-nerve-flossing-and-how-it-can-help-you
- https://www.btetechnologies.com/therapyspark/nerve-flossing/
- https://lytyoga.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/image1.png
- https://www.yorkvillesportsmed.com/blog/ultimate-guide-to-nerve-flossing-and-how-it-can-help-you
- https://chiroup.com/blog/3-simple-nerve-flossing-exercises-to-help-resolve-arm-pain
- https://www.yorkvillesportsmed.com/blog/ultimate-guide-to-nerve-flossing-and-how-it-can-help-you
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/nerve-flossing-in-physical-therapy-4797516
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/nerve-flossing
- https://myevolvechiropractor.com/introduction-to-nerve-flossing/
- https://kibowhope.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/The-Hope-Blog-Posts-1.png
- https://www.lifewire.com/best-workout-log-apps-4140222
- https://albanychiroandpt.com/top-4-fitness-technologies-to-track-your-exercise/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2565076/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9848316/
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/nerve-flossing
- https://chiroup.com/blog/4-simple-nerve-flossing-exercises-to-help-resolve-back-leg-pain
